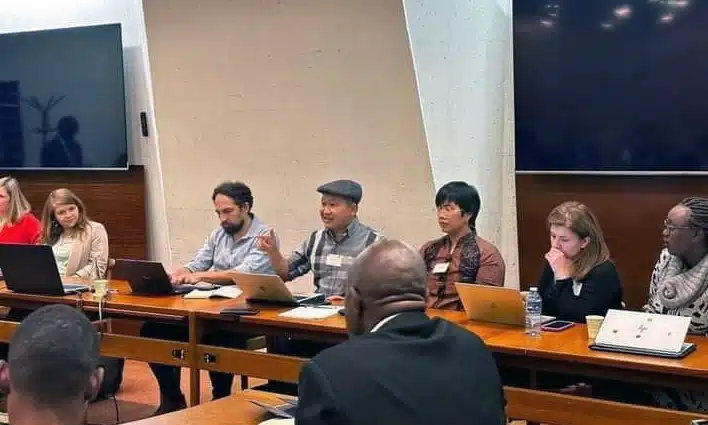
UNDIP, Semarang (October 7, 2025) – Universitas Diponegoro (UNDIP) once again held a scientific paper presentation featuring four UNDIP professor candidates, organized by the UNDIP Board of Professors on Tuesday, October 7, 2025, at 1:00 PM, in the Academic Senate Meeting Room, 3rd Floor of the SA-MWA Building, UNDIP Tembalang Campus.
The four professor candidates were Dr. Ir. Budi Setiyana, M.T., from the Faculty of Engineering; Dr. Ir. Suryono, M.Sc., from the Faculty of Fisheries and Marine Science; Ojo Kurdi, S.T., M.T., Ph.D., from the Faculty of Engineering; and Dr. Ahyar Yuniawan, S.E., M.Si., from the Faculty of Economics and Business.
In the first presentation, Dr. Ir. Budi Setiyana, M.T., discussed his scientific study titled “Improving the Reliability of Sliding Bearings by Reducing Noise and Vibration through Surface Modification Techniques.” The research examined strategies to enhance the performance of sliding bearings through surface modification engineering approaches. The discussion focused on the application of tribology principles to address key issues such as wear, noise, and vibration caused by turbulence and cavitation in lubricants.
Various modification methods were explored, including surface roughness control, multi-step texturing, and hydrophobic coatings to create slip-boundary conditions that reduce friction and increase load-carrying capacity. The study also integrated the Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) approach into Elastohydrodynamic (EHD) systems to produce more realistic modeling of lubricant-structure interactions. The findings indicated that these modification techniques are not only effective in reducing noise and vibration but also extend bearing lifespan and improve reliability in high-speed industrial applications.
The second presentation by Dr. Ir. Suryono, M.Sc., was titled “The Urgency of Implementing Adaptive Conservation to Build Coastal and Small Island Resilience in Indonesia.” In this study, Dr. Suryono discussed the need to shift from conventional conservation toward adaptive conservation as a more effective, inclusive, and sustainable strategy for managing coastal ecosystems. He explained that Indonesia’s coastal areas and small islands face dual pressures from anthropogenic activities and global climate change, leading to severe degradation of key ecosystems such as mangrove forests, seagrass beds, and coral reefs. Adaptive conservation offers an alternative solution with approaches that respond dynamically to environmental and social changes.
This approach emphasizes continuous learning, policy adjustments based on field monitoring, and active community participation as an integral part of coastal resource governance. By integrating ecological and social systems, adaptive conservation not only aims to maintain environmental balance but also to build the resilience of coastal communities so they can survive and thrive amid climate challenges. Its implementation is expected to ensure the sustainability of coastal resources, improve community welfare, and support the achievement of sustainable development goals in Indonesia.
In the third presentation, Ojo Kurdi, S.T., M.T., Ph.D., delivered his research titled “The Contribution of Failure Analysis to Enhancing the Reliability and Energy Efficiency of Machine Components Toward National Independence in Automotive and Industrial Machinery Technology.” He highlighted the importance of failure analysis and surface engineering in improving the reliability, energy efficiency, and lifespan of machine components. Ojo emphasized that technological independence in the national automotive sector must be built through mastery of component design and manufacturing, with a focus on identifying critical failure points using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and experimental testing.
Surface engineering techniques such as laser micromachining and functional coating are employed to reduce friction and wear and to improve thermal performance in components such as bearings and gears. By integrating structural analysis and surface engineering, the study produces stronger, more energy-efficient, and longer-lasting component designs. The research also opens opportunities for the use of lightweight materials, topology optimization, and intelligent monitoring to support modern vehicle development.
The final presentation was delivered by Dr. Ahyar Yuniawan, S.E., M.Si., titled “Digital Business Communication Strategies to Enhance MSME Competitiveness in the Era of Digital Transformation.” Dr. Ahyar comprehensively discussed the importance of applying digital business communication strategies as a key to improving the competitiveness of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) amid rapid digital transformation. He explained that while MSMEs play a strategic role in the national economy, they still face challenges such as limited digital literacy, insufficient use of information technology, and difficulties in building brand image and consumer trust in the digital space. To address these challenges, digital business communication strategies must be designed in an integrated manner, utilizing various digital platforms such as social media, online marketplaces, websites, and customer-based communication applications.
Dr. Ahyar emphasized the importance of digital branding, business storytelling, and two-way consumer engagement as part of effective communication strategies. These approaches not only increase brand visibility and reputation but also foster long-term relationships based on trust and customer loyalty. He also emphasized the importance of digital data analysis in understanding consumer behavior and enabling evidence-based marketing decisions. With adaptive and sustainable communication strategies, MSMEs can optimize their digital market potential, expand their reach, and strengthen their competitiveness both locally and globally.
The scientific works presented by these four professor candidates are closely aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), SDG 7 (Clean Energy), SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), SDG 13 (Climate Action), SDG 14 (Life Below Water), and SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities).
This scientific presentation is one of the required steps for lecturers to attain the academic title of Professor. Through this presentation, the candidates demonstrate their scientific contributions and the relevance of their research to societal needs—reflecting UNDIP’s tagline, “UNDIP Noble and Valuable.” (Public Communication/UNDIP/Syahra)